A neuropathologist has examined the brains of 111 N.F.L. players — and 110 were found to have C.T.E., the degenerative disease linked to repeated blows to the head.
By Joe Ward, Josh Williams and Sam Manchester
July 25, 2017
Dr. Ann McKee, a neuropathologist, has examined the brains of 202 deceased football players. A broad survey of her findings was published on Tuesday in The Journal of the American Medical Association.
Of the 202 players, 111 of them played in the N.F.L. — and 110 of those were found to have chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or C.T.E., the degenerative disease believed to be caused by repeated blows to the head.
C.T.E. causes myriad symptoms, including memory loss, confusion, depression and dementia. The problems can arise years after the blows to the head have stopped.
The brains here are from players who died as young as 23 and as old as 89. And they are from every position on the field — quarterbacks, running backs and linebackers, and even a place-kicker and a punter.
They are from players you have never heard of and players, like Ken Stabler, who are enshrined in the Hall of Fame. Some of the brains cannot be publicly identified, per the families’ wishes.
The image above is from the brain of Ronnie Caveness, a linebacker for the Houston Oilers and Kansas City Chiefs. In college, he helped the Arkansas Razorbacks go undefeated in 1964. One of his teammates was Jerry Jones, now the owner of the Dallas Cowboys. Jones has rejected the belief that there is a link between football and C.T.E.
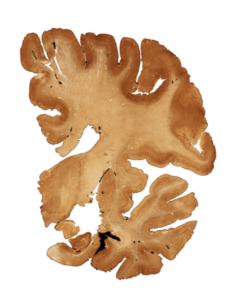
The image above is from the brain of Ollie Matson, who played 14 seasons in the N.F.L. — after winning two medals on the track at the 1952 Helsinki Games. He died in 2011 at age 80 after being mostly bedridden with dementia, his nephew told The Associated Press, adding that Matson hadn’t spoken in four years.
Dr. McKee, chief of neuropathology at the VA Boston Healthcare System and director of the CTE Center at Boston University, has amassed the largest C.T.E. brain bank in the world. But the brains of some other players found to have the disease — like Junior Seau, Mike Webster and Andre Waters — were examined elsewhere.
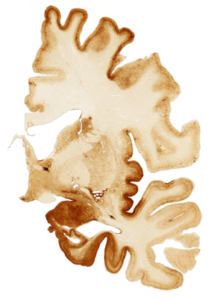
The image above is from the brain of Ollie Matson, who played 14 seasons in the N.F.L. — after winning two medals on the track at the 1952 Helsinki Games. He died in 2011 at age 80 after being mostly bedridden with dementia, his nephew told The Associated Press, adding that Matson hadn’t spoken in four years.
Dr. McKee, chief of neuropathology at the VA Boston Healthcare System and director of the CTE Center at Boston University, has amassed the largest C.T.E. brain bank in the world. But the brains of some other players found to have the disease — like Junior Seau, Mike Webster and Andre Waters — were examined elsewhere.
The set of players posthumously tested by Dr. McKee is far from a random sample of N.F.L. retirees. “There’s a tremendous selection bias,” she has cautioned, noting that many families have donated brains specifically because the former player showed symptoms of C.T.E.
But 110 positives remain significant scientific evidence of an N.F.L. player’s risk of developing C.T.E., which can be diagnosed only after death. About 1,300 former players have died since the B.U. group began examining brains. So even if every one of the other 1,200 players had tested negative — which even the heartiest skeptics would agree could not possibly be the case — the minimum C.T.E. prevalence would be close to 9 percent, vastly higher than in the general population.
The N.F.L.’s top health and safety official has acknowledged a link between football and C.T.E., and the league has begun to steer children away from playing the sport in its regular form, encouraging safer tackling methods and promoting flag football.
lesen Sie weiter:
https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2017/07/25/sports/football/nfl-cte.html
